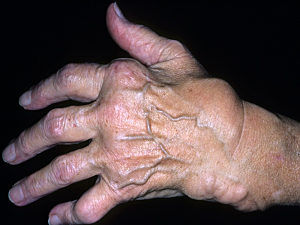
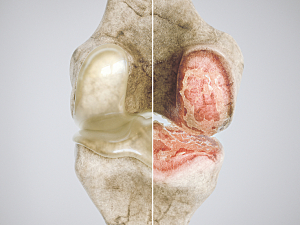
How Might ICI Therapy Lead to Checkpoint Inhibitor-associated Arthritis?
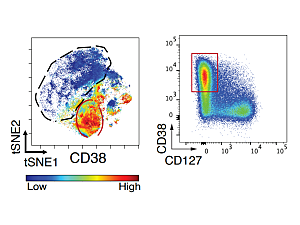
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapies have revolutionized the treatment of advanced cancers, but they have a downside. Rheumatologist Deepak A. Rao, MD, PhD, is part of a study examining the rheumatologic manifestation of checkpoint inhibitor-associated arthritis in patients treated with a specific ICI therapy.
Read More...