Megakaryocytes Contribute to Systemic Inflammation in Arthritis
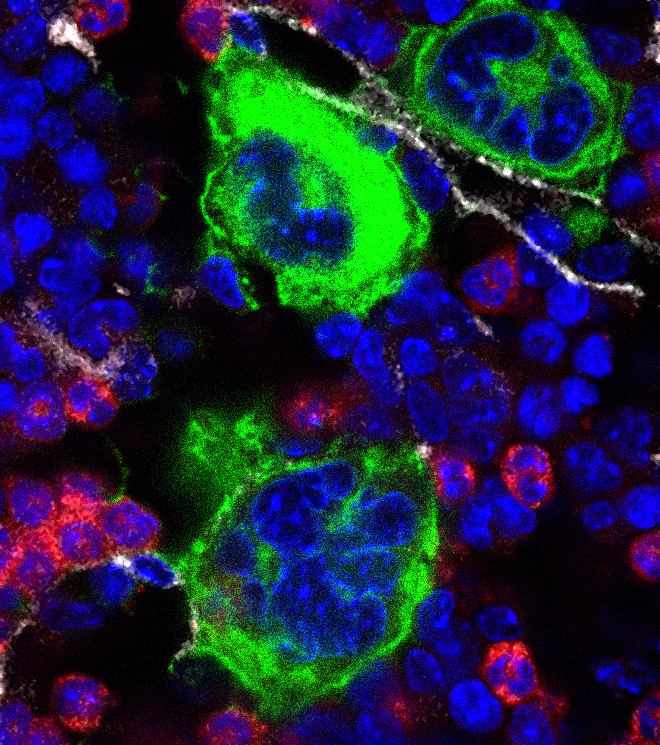
How does a healthy joint become inflamed? This question has engaged laboratories worldwide for decades, yet surprises continue. A particularly unexpected development emerged recently from the laboratory of Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) rheumatologist Peter Nigrovic, MD, (www.nigroviclab.org) which implicated a lineage that until now has been of interest primarily to hematologists: the megakaryocyte. Read More

