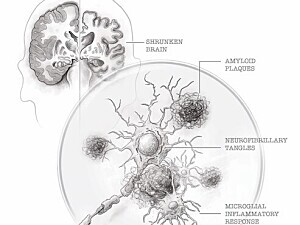
Telemedicine Extends Brigham’s Rich History of Neurosurgical Innovation to Underserved Areas

Advances in telemedicine are enabling the Brigham to bring high-quality neurosurgical care to patients nationally and internationally. Timothy R. Smith, MD, PhD, MPH, of the Department of Neurosurgery, discusses how these efforts reflect the broader movement to meet patients’ right to healthcare globally.
Read More...